Bacillus anthracis is the etiologic agent of anthrax â€" a common disease of livestock and, occasionally, of humans â€" and the only obligate pathogen within the genus Bacillus. B. anthracis is a Gram-positive, endospore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium, with a width of 1.0â€"1.2 µm and a length of 3â€"5 µm. It can be grown in an ordinary nutrient medium under aerobic or anaerobic conditions.
It is one of few bacteria known to synthesize a protein capsule (poly-D-gamma-glutamic acid). Like Bordetella pertussis, it forms a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase exotoxin known as (edema factor), along with lethal factor. It bears close genotypical and phenotypical resemblance to Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. All three species share cellular dimensions and morphology. All form oval spores located centrally in an unswollen sporangium. B. anthracis spores, in particular, are highly resilient, surviving extremes of temperature, low-nutrient environments, and harsh chemical treatment over decades or centuries.
The spore is a dehydrated cell with thick walls and additional layers that form inside the cell membrane. It can remain inactive for many years, but if it comes into a favorable environment, it begins to grow again. It is sometimes called an endospore because it initially develops inside the rod-shaped form. Features such as the location within the rod, the size and shape of the endospore, and whether or not it causes the wall of the rod to bulge out are characteristic of particular species of Bacillus. Depending upon the species, the endospores are round, oval, or occasionally cylindrical. They are highly refractile and contain dipicolinic acid. Electron micrograph sections show they have a thin outer spore coat, a thick spore cortex, and an inner spore membrane surrounding the spore contents. The spores resist heat, drying, and many disinfectants (including 95% ethanol). Because of these attributes, B. anthracis spores are extraordinarily well-suited to use (in powdered and aerosol form) as biological weapons. Such weaponization has been accomplished in the past by at least five state bioweapons programs â€" those of the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, Russia, and Iraq â€" and has been attempted by several others.
Historical background
French physician Casimir Davaine (1812-1882) demonstrated the symptoms of anthrax were invariably accompanied by the microbe B. anthracis. German physician Aloys Pollender (1799â€"1879) is also credited for this discovery. B. anthracis was the first bacterium conclusively demonstrated to cause disease, by Robert Koch in 1876. The species name anthracis is from the Greek anthrax (ἄνθÏαξ), meaning "coal" and referring to the most common form of the disease, cutaneous anthrax, in which large, black skin lesions are formed.
Genome structure

B. anthracis has a single chromosome which is a circular, 5,227,293-bp DNA molecule. It also has two circular, extrachromosomal, double-stranded DNA plasmids, pXO1 and pXO2. Both the pXO1 and pXO2 plasmids are required for full virulence and represent two distinct plasmid families.
pXO1 plasmid
The pXO1 plasmid (182 kb) contains the genes that encode for the anthrax toxin components: pag (protective antigen, PA), lef (lethal factor, LF), and cya (edema factor, EF). These factors are contained within a 44.8-kb pathogenicity island (PAI). The lethal toxin is a combination of PA with LF and the edema toxin is a combination of PA with EF. The PAI also contains genes which encode a transcriptional activator AtxA and the repressor PagR, both of which regulate the expression of the anthrax toxin genes.
pXO2 plasmid
pXO2 encodes a five-gene operon (capBCADE) which synthesizes a poly-γ-D-glutamic acid (polyglutamate) capsule. This capsule allows B. anthracis to evade the host immune system by protecting itself from phagocytosis. Expression of the capsule operon is activated by the transcriptional regulators AcpA and AcpB, located in the pXO2 pathogenicity island (35 kb). Interestingly, AcpA and AcpB expression are under the control of AtxA from pXO1.
Strains

The 89 known strains of B. anthracis include:
- Sterne strain (34F2; aka the "Weybridge strain"), used by Max Sterne in his 1930s vaccines
- Vollum strain, formerly weaponized by the US, UK, and Iraq; isolated from cow in Oxfordshire, UK, in 1935
- Vollum M-36, virulent British research strain; passed through macaques 36 times
- Vollum 1B, weaponized by the US and UK in the 1940s-60s
- Vollum-14578, UK biotesting contaminated Gruinard Island, Scotland, in 1940s
- V770-NP1-R, the avirulent, nonencapsulated strain used in the BioThrax vaccine
- Anthrax 836, highly virulent strain weaponized by the USSR; discovered in Kirov in 1953
- Ames strain, isolated from a cow in Texas in 1981; famously used in AMERITHRAX letter attacks (2001)
- Ames Ancestor
- Ames Florida
- H9401, isolated from human patient in Korea; used in investigational anthrax vaccines
Evolution

Whole genome sequencing has made reconstruction of the B. anthracis phylogeny extremely accurate. A contributing factor to the reconstruction is B. anthracis being monomorphic, meaning it has low genetic diversity, including the absence of any measurable lateral DNA transfer since its derivation as a species. The lack of diversity is due to a short evolutionary history that has precluded mutational saturation in single nucleotide polymorphisms.
A short evolutionary time does not necessarily mean a short chronological time. When DNA is replicated, mistakes occur which become genetic mutations. The buildup of these mutations over time leads to the evolution of a species. During the B. anthracis lifecycle, it spends a significant amount of time in the soil spore reservoir stage, a stage in which DNA replication does not occur. These prolonged periods of dormancy have greatly reduced the evolutionary rate of the organism.
Nearest neighbors
B. anthracis belongs to the B. cereus group consisting of the strains: B. cereus, B. anthracis, B. thuringiensis, B. weihenstephanensis, B. mycoides, and B. pseudomycoides. The first three strains are pathogenic or opportunistic to insects or mammals, while the last three are not considered pathogenic. The strains of this group are genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous overall, but some of the strains are more closely related and phylogenetically intermixed at the chromosome level. The B. cereus group generally exhibits complex genomes and most carry varying numbers of plasmids.
B. cereus is a soil-dwelling bacterium which can colonize the gut of invertebrates as a symbiont and is a frequent cause of food poisoning It produces an emetic toxin, enterotoxins, and other virulence factors. The enterotoxins and virulence factors are encoded on the chromosome, while the emetic toxin is encoded on a 270-kb plasmid, pCER270.
B. thuringiensis is an insect pathogen and is characterized by production of parasporal crystals of insecticidal toxins Cry and Cyt. The genes encoding these proteins are commonly located on plasmids which can be lost from the organism, making it indistinguishable from B. cereus.
Pseudogene
PlcR is a global transcriptional regulator which controls most of the secreted virulence factors in B. cereus and B. thuringiensis. It is chromosomally encoded and is ubiquitous throughout the cell. In B. anthracis, however, the plcR gene contains a single base change at position 640, a nonsense mutation, which creates a dysfunctional protein. While 1% of the B. cereus group carries an inactivated plcR gene, none of them carries the specific mutation found only in B. anthracis.
The plcR gene is part of a two-gene operon with papR. The papR gene encodes a small protein which is secreted from the cell and the reimported as a processed heptapeptide forming a quorum-sensing system. The lack of PlcR in B. anthracis is a principle characteristic differentiating it from other members of the B. cereus group. While B. cereus and B. thuringiensis depend on the plcR gene for expression of their virulence factors, B. anthracis relies on the pXO1 and pXO2 plasmids for its virulence.
Clinical aspects
Pathogenesis
B. anthracis possesses an antiphagocytic capsule essential for full virulence. The organism also produces three plasmid-coded exotoxins: edema factor, a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase, causes elevation of intracellular cAMP, and is responsible for the severe edema usually seen in B. anthracis infections; lethal toxin is responsible for tissue necrosis; protective antigen (so named because of its use in producing protective anthrax vaccines) mediates cell entry of edema factor and lethal toxin.
Manifestations in human disease
Three forms of human anthrax disease are recognized based on their portal of entry.
- Cutaneous, the most common form (95%), causes a localized, inflammatory, black, necrotic lesion (eschar).
- Pulmonary, the highly fatal form, is characterized by sudden, massive chest edema followed by cardiovascular shock.
- Gastrointestinal, a rare but also fatal (causes death to 25%) type, results from ingestion of spores.
Prevention and treatment
A number of anthrax vaccines have been developed for preventive use in livestock and humans. Infections with B. anthracis can be treated with β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillin, and others which are active against Gram-positive bacteria. Penicillin-resistant B. anthracis can be treated with fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin or tetracycline antibiotics such as doxycycline.
Laboratory research
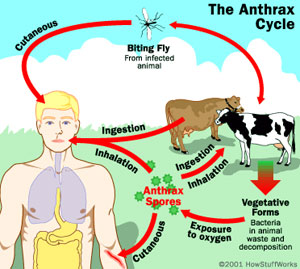
Components of tea, such as polyphenols, have the ability to inhibit the activity both of B. anthracis and its toxin considerably; spores, however, are not affected. The addition of milk to the tea completely inhibits its antibacterial activity against anthrax. Activity against the B. athracis in the laboratory does not prove that drinking tea affects the course of an infection, since it is unknown how these polyphenols are absorbed and distributed within the body.
Recent research
Advances in genotyping methods have led to improved genetic analysis for variation and relatedness. These methods include multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis (MLVA) and typing systems using canonical single-nucleotide polymorphisms. The Ames ancestor chromosome was sequenced in 2003 and contributes to the identification of genes involved in the virulence of B. anthracis. Recently, B. anthracis isolate H9401 was isolated from a Korean patient suffering from gastrointestinal anthrax. The goal of the Republic of Korea is to use this strain as a challenge strain to develop a recombinant vaccine against anthrax.
The H9401 strain isolated in the Republic of Korea was sequenced using 454 GS-FLX technology and analyzed using several bioinformatics tools to align, annotate, and compare H9401 to other B. anthracis strains. The sequencing coverage level suggests a molecular ratio of pXO1:pXO2:chromosome as 3:2:1 which is identical to the Ames Florida and Ames Ancestor strains. H9401 has 99.679% sequence homology with Ames Ancestor with an amino acid sequence homology of 99.870%. H9401 has a circular chromosome (5,218,947 bp with 5,480 predicted ORFs), the pXO1 plasmid (181,700 bp with 202 predicted ORFs), and the pXO2 plasmid (94,824 bp with 110 predicted ORFs). As compared to the Ames Ancestor chromosome above, the H9401 chromosome is about 8.5 kb smaller. Due to the high pathogenecity and sequence similarity to the Ames Ancestor, H9401 will be used as a reference for testing the efficacy of candidate anthrax vaccines by the Repbulic of Korea.
Host interactions
As with most other pathogenic bacteria, B. anthracis must acquire iron to grow and proliferate in its host environment. The most readily available iron sources for pathogenic bacteria are the heme groups used by the host in the transport of oxygen. To scavenge heme from host hemoglobin and myoglobin, B. anthracis uses two secretory siderophore proteins, IsdX1 and IsdX2. These proteins can separate heme from hemoglobin, allowing surface proteins of B. anthracis to transport it into the cell.
References
External links

- Bacillus anthracis genomes and related information at PATRIC, a Bioinformatics Resource Center funded by NIAID
- Hazards in Animal Research Database - Bacillus anthracis
- Pathema-Bacillus Resource







I'm 61 years old, I contracted hpv in 2011' I has be taking lot treatment for it and some months ago the wart stated coming out seriously, I used lot recommendation because there was lot warts around my anus and was so embarrassed. but today I'm totally happy I got the virus eliminated by using natural treatment from Dr Onokun herbal center after his treatment I got cured. all the warts went away' seriously believed Dr Onokun he have the cure for human papillomavirus because he has eliminated hpv been in my body since 2011, Dr Onokun make it possible for me. Here is Dr Onokun email to reach him: Dronokunherbalcure@gmail.com he is welled capable of curing terrible diseases.
ReplyDeleteHappiness is all i see now I never thought that I will live on
ReplyDeleteearth before the year runs out. I have been suffering from a
deadly disease (Herpes) for the past 3 years now; I had spent
a lot of money going from one places to another, from
churches to churches, hospitals have been my home every day
residence. Constant checks up have been my hobby not until
this faithful day, I was searching through the internet, I saw a
testimony on how pp him +2348154637647 Dr Lucky, helped
someone in curing his Herpes disease, quickly I copied his
email which is (drluckyherbalcure@gmail.com) just to give
him a test I spoke to him, he asked me to do some certain
things which I did, he told me that he is going to provide the
herbal cure to me, which he did, then he asked me to go for
medical checkup after some days after using the herbal cure, I
was free from the deadly disease, he only asked me to post
the testimony through the whole world, faithfully am doing it
now, please brothers and sisters, he is great, I owe him in
return. if you are having a similar problem just email him on
(drluckyherbalcure@gmail.com) or Call him or WhatsApp him
+2348154637647
Can't still believe that i got cured from Genital Herpes through herbal treatment from Dr LUCKY who I met through the internet, I actually couldn't believe it at first because it sounded impossible to me knowing how far I have gone just to get rid of it. Dr LUCKY send me his medicine which I took as instructed and here I am living a happy life once again, a big thanks to Dr LUCKY , I am sure there are many herbal doctors out there but Dr LUCKY did it for me, contact him on Email him; { drluckyherbalcure@gmail.com }
ReplyDeleteherpes is a serious and recurring disease which can't be cured through drugs or injections by the American doctors but the best way to deal with herpes is by taking natural herbs medicine for it and is only few American doctors that know about this herbal medicine from Dr Akhanene .. I have read about Dr Akhanene the great herbalist doctor from African who can cure disease with his powerful herbal medicine. for the people suffering from the following diseases, Herpes, Cancer, Also,Herpatitis, Diabetes, Hps,Infections ETC should contact him for his herbal medicine because i am a living testimony and i was cured of herpes. Although, i sent him what he requested and he sent me his medicine which i took for 1 weeks and today when i went for test i was tested herpes negative. you can reach him through his Emai drakhanenespellhome@gmail.com.com or whatsapp or call him +2348168714427
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteA friend of mine recommended me to contact this herbal Doctor for herpes cure and he asked me to purchase his herbal medicine which i did, when i received this herbal medicine, he gave me instructions on how to use it, after taking the medicine as instructed for 2 weeks, i went for check up and the result shows negative and i was cured of herpes, I am now free from Herpes. You can contact him on his email …………His result is 💯💯💯💯💯 guaranteed. I highly recommend..........
You can win your Ex lover back in 48 hours just like me.
Very effective ...
For fast and reliable solution.
Get boyfriend back after break up.
Get girlfriend back after break up.
Get Gay partner back.
Get Lesbian partner back.
Make Your Husband/Wife love you Forever.
Stop Having Bad Dreams.
Make Women/Men To Run After You.
Stop Divorce from happening.
Divorce Your Husband/Wife.
Make Partner marry you.
Make Wishes To Be Granted.
Win Court Case/Law suit.
Get pregnant.
Luck To Win A Lottery.
Stop Marriage/Relationship from Breaking Apart.
I used his herbal remedy to cure Hsv-2..
100% result guaranteed..
Email R.buckler11 (( @gmail .com))…………